 The increasing prevalence of hip arthrosis, commonly known as
osteoarthritis of the hip, has become a significant health concern globally.
According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, hip osteoarthritis affects over
200 million individuals worldwide, leading to
reduced mobility and quality of life.
The Hip Arthrosis System has emerged as a pivotal
approach in mitigating the effects of this debilitating condition.
With advancements in medical technology and rehabilitation strategies,
this system not only aims to improve joint function but also enhances overall mobility for patients.
Research indicates that effective management through the Hip Arthrosis System can lead to a
reduction in pain levels by up to 50% and significantly
improve daily activities for individuals affected by hip arthrosis.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various aspects of the Hip Arthrosis System,
providing insights on its application and benefits in enhancing mobility for those suffering from
this common yet challenging ailment.
The increasing prevalence of hip arthrosis, commonly known as
osteoarthritis of the hip, has become a significant health concern globally.
According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, hip osteoarthritis affects over
200 million individuals worldwide, leading to
reduced mobility and quality of life.
The Hip Arthrosis System has emerged as a pivotal
approach in mitigating the effects of this debilitating condition.
With advancements in medical technology and rehabilitation strategies,
this system not only aims to improve joint function but also enhances overall mobility for patients.
Research indicates that effective management through the Hip Arthrosis System can lead to a
reduction in pain levels by up to 50% and significantly
improve daily activities for individuals affected by hip arthrosis.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various aspects of the Hip Arthrosis System,
providing insights on its application and benefits in enhancing mobility for those suffering from
this common yet challenging ailment.
Hip arthrosis, commonly known as osteoarthritis of the hip, is a degenerative joint disease that affects millions worldwide. According to the Global Burden of Disease Study, hip osteoarthritis ranks among the top ten causes of disability in adults over 50 years. This condition is characterized by the gradual wear and tear of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion. By age 65, approximately 50% of individuals experience some level of hip discomfort, emphasizing the urgent need for effective management strategies.
Research highlights the critical role of early intervention in hip arthrosis. A study published in the Journal of Clinical Orthopaedics and Trauma indicates that 15% of patients report significant improvement in mobility and pain reduction when treatment starts at the first signs of hip discomfort. Non-surgical approaches, including physical therapy, weight management, and the use of assistive devices, are essential in enhancing mobility for those affected. The Hip Arthrosis System utilizes these strategies to create a personalized rehabilitation program tailored to the individual’s needs, ultimately fostering improved mobility and quality of life.
Hip arthrosis, also known as osteoarthritis of the hip, is a degenerative joint disease that often manifests with key symptoms, making early diagnosis crucial for effective management. Typical signs include hip pain, stiffness, particularly in the morning, and reduced range of motion. According to the Arthritis Foundation, approximately 27 million Americans are affected by osteoarthritis, highlighting the commonality of hip-related joint issues. As the cartilage wears down over time, these symptoms can become increasingly pronounced, significantly impacting mobility and quality of life.
Seeking treatment for hip arthrosis should be considered when symptoms escalate beyond manageable levels or adversely affect daily life. The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons emphasizes that an active lifestyle, recognized as essential for joint health, may become untenable with advanced hip arthrosis. Timely intervention can include non-surgical methods such as physical therapy, pain relief medications, or corticosteroid injections, and in severe cases, surgical options like hip replacement may be recommended. Understanding when to seek professional advice can lead to more effective management strategies and improved mobility outcomes.
This chart illustrates the average mobility scores of individuals with hip arthrosis across different age groups. As age increases, there is a noticeable decline in average mobility, indicating the potential impact of hip arthrosis on daily function.
The Hip Arthrosis System comprises various components designed to enhance mobility for individuals suffering from osteoarthritis, particularly in the hip joint. This system includes custom-made orthotics that cater to abnormal walking patterns, which can result from joint degeneration. These orthotics not only provide support but can also help correct gait issues, thereby contributing to improved balance and reduced pain during movement.
In addition to orthotics, the Hip Arthrosis System may incorporate lifestyle interventions, such as dietary adjustments and physical therapy. Certain foods known for their anti-inflammatory properties may be included in a patient’s diet to help manage pain. Turmeric, for instance, contains curcumin, which has shown potential in alleviating inflammation.
Furthermore, incorporating supplements that support joint health can be beneficial for individuals aiming to maintain mobility. Together, these components create a comprehensive approach to managing hip arthrosis, focusing on both alleviating symptoms and enhancing overall functional capacity.
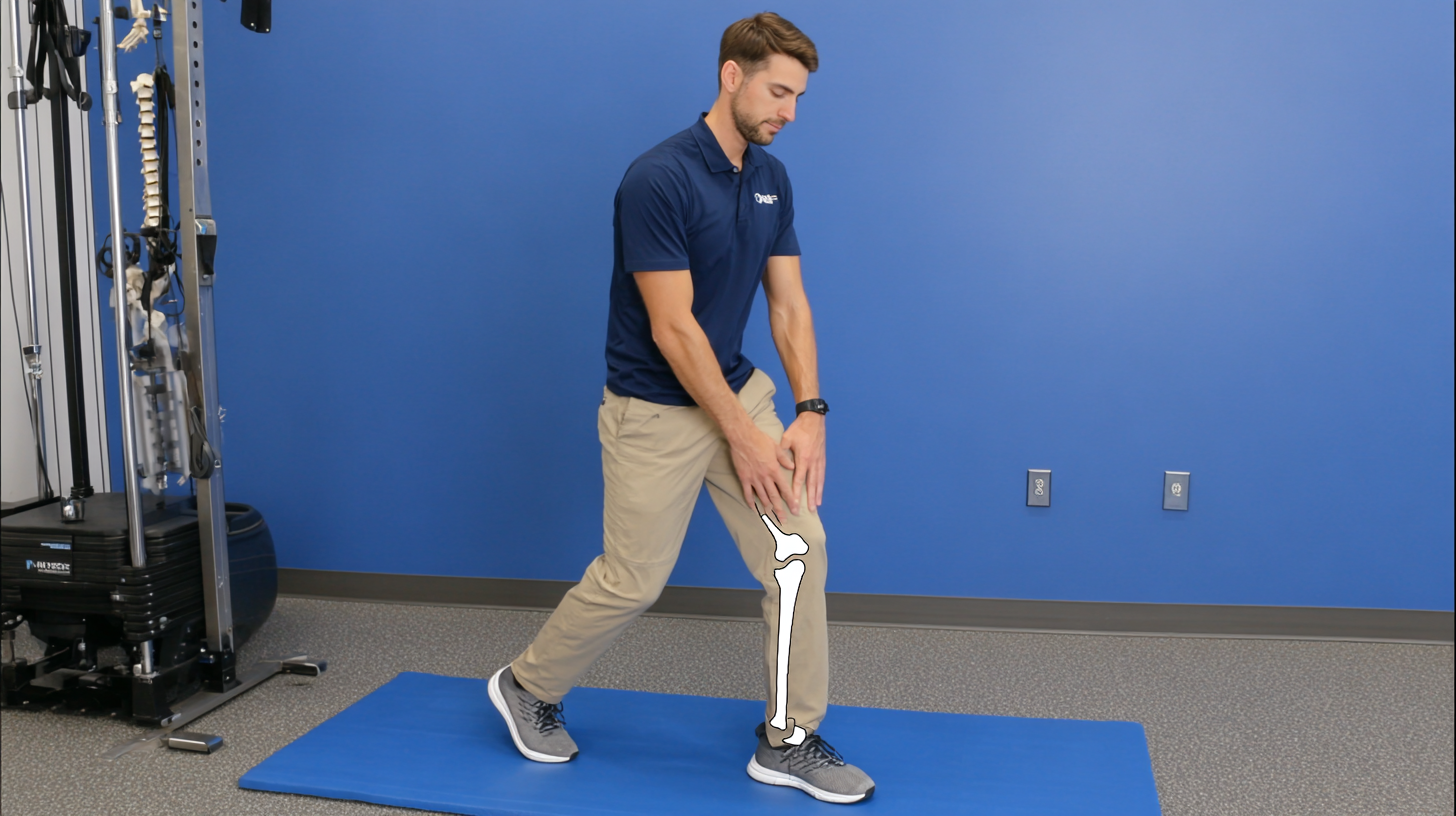 Effective exercises and rehabilitation techniques play a crucial role in enhancing mobility, particularly for individuals dealing with hip arthrosis. Strengthening the muscles around the hip joint is essential for improving overall mobility and reducing pain. Engaging in targeted exercises helps support joint function and alleviates discomfort, enabling better movement. A combination of stretching and strengthening routines can significantly benefit those experiencing limitations due to hip issues.
Effective exercises and rehabilitation techniques play a crucial role in enhancing mobility, particularly for individuals dealing with hip arthrosis. Strengthening the muscles around the hip joint is essential for improving overall mobility and reducing pain. Engaging in targeted exercises helps support joint function and alleviates discomfort, enabling better movement. A combination of stretching and strengthening routines can significantly benefit those experiencing limitations due to hip issues.
Additionally, incorporating balance training into rehabilitation can enhance stability and prevent falls, a common concern among individuals with joint pain. Recent studies emphasize the importance of tailored exercise interventions, which not only improve mobility but also foster independence in daily activities. Simple mobility routines, such as dynamic stretches and strengthening exercises, can be seamlessly integrated into a daily regimen, ensuring continued improvement and engagement in physical activity, ultimately leading to a healthier, more active lifestyle.
Maintaining hip health is crucial for enhancing mobility, especially for individuals suffering from hip arthrosis. Preventive measures play a significant role in minimizing the progression of this condition. Engaging in low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can strengthen the muscles around the hip joint without causing additional stress. Incorporating flexibility and stretching routines can also improve range of motion and reduce stiffness. Moreover, maintaining a healthy weight is essential, as excess weight places additional strain on the hips, potentially exacerbating arthritic symptoms.
In addition to physical activity, lifestyle changes can significantly support hip health. A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fatty fish, fruits, and vegetables, can help manage inflammation and provide essential nutrients for joint health. Adequate hydration is also vital, as it supports cartilage health. Furthermore, practicing good posture and using assistive devices when needed can prevent undue stress on the hips. Ultimately, these lifestyle modifications not only enhance mobility but also contribute to overall well-being, empowering individuals to lead active and fulfilling lives despite hip arthrosis.
| Dimension | Description |
|---|---|
| Preventive Measures | Regular low-impact exercise to strengthen hip muscles. |
| Weight Management | Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce joint stress. |
| Nutrition | Balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. |
| Physical Therapy | Engaging in personalized movement strategies and strength training. |
| Hydration | Staying well-hydrated to maintain joint lubrications. |
| Comfortable Footwear | Wearing shoes that provide good support and cushioning. |
| Stress Management | Practicing relaxation techniques to reduce muscle tension. |



*The content on this website is for general informational purposes only and should not be taken as medical advice. Please contact your physician or therapist to learn what therapy solution is suitable for your specific needs. Not all products, features, or indications shown are approved in all countries.